Understanding network utilities is crucial for anyone involved in system administration, cybersecurity, or networking. This article will guide you on How to Use Netcat (nc) Command with Examples, a powerful tool often called the “network Swiss army knife.” We will explore its functionalities, from Basic port scanning to establishing simple chat servers and transferring files. By the end, you will have a solid grasp of Netcat’s capabilities and practical applications.
Introduction: Understanding the Netcat (nc) Command
Netcat, commonly referred to as `nc`, is a versatile command-line utility. It reads and writes data across network connections using TCP or UDP protocols. This tool is fundamental for network debugging and exploration. Therefore, mastering its use can significantly enhance your network troubleshooting skills.
What is Netcat (nc)? A Brief Overview
Netcat is a featured networking utility that provides a simple Unix program. It creates network connections, sends arbitrary data, and listens on specific ports. Furthermore, it supports both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing. This makes it an indispensable tool for many network-related tasks.
Why Learn How to Use Netcat? Its Importance in Networking
Learning How to Use Netcat (nc) Command with Examples offers immense benefits. It allows users to perform various tasks, including port scanning, network debugging, and creating simple backdoors. Moreover, its flexibility makes it a favorite among penetration testers and system administrators. Understanding Netcat helps in diagnosing connectivity issues and testing network services effectively.
What is Netcat (nc) and Its Core Functionality?
Netcat’s core functionality revolves around its ability to establish and listen for network connections. It can act as both a client and a server. This dual capability makes it incredibly powerful. Additionally, it supports various options to control connection behavior and data transfer.
Netcat’s Role as a Network Swiss Army Knife
Netcat earns its “Swiss army knife” moniker due to its wide range of applications. It can perform simple tasks like checking if a port is open. However, it also handles complex operations such as setting up a basic web server. Its adaptability ensures it remains a go-to tool for many network professionals.
Common Use Cases for the `nc` Command
The `nc` command has numerous practical applications. These include:
- Port Scanning: Identifying open ports on a target system.
- File Transfer: Sending files securely between two machines.
- Chat Server: Creating simple, real-time communication channels.
- Network Debugging: Testing connectivity and service responses.
- Proxying: Forwarding network traffic.
Each use case highlights the utility’s versatility and power.
History and Evolution of Netcat
Netcat was originally developed by Hobbit in 1995. It quickly gained popularity due to its simplicity and effectiveness. Over the years, several versions and forks have emerged, including OpenBSD Netcat and GNU Netcat. These variations often add new features or improve security. Nevertheless, the core functionality remains consistent across implementations.
Basic Netcat (nc) Command Syntax and Essential Options
Understanding the basic syntax is the first step to effectively use Netcat. The command structure is straightforward, yet powerful. Furthermore, combining different options unlocks its full potential. This section will detail the fundamental components.
Understanding `nc` Command Syntax and Structure
The general syntax for the `nc` command is `nc [options] [hostname] [port(s)]`. For instance, to connect to a server, you specify the hostname and port. To listen for connections, you use specific options like `-l`. This simple structure allows for complex operations.
Key Netcat Options Explained: `-l`, `-p`, `-v`, `-z`, `-u`
Several key options control Netcat’s behavior. Here are some essential ones:
-l(listen): Puts Netcat in listen mode, waiting for incoming connections.-p [port](port): Specifies the source port to use.-v(verbose): Provides more detailed output, useful for debugging.-z(zero-I/O): Used for port scanning without sending any data.-u(UDP): Uses UDP instead of the default TCP protocol.
These options are frequently combined to achieve specific tasks.
Installation and Availability of Netcat on Different OS
Netcat is widely available across various operating systems. On Linux distributions, it often comes pre-installed or can be installed via package managers (e.g., `sudo apt install netcat`). For Windows, you can download pre-compiled binaries. macOS users can install it using Homebrew (`brew install netcat`). This broad availability ensures accessibility for all users.
Practical Examples: How to Use Netcat for Port Scanning
Port scanning is one of Netcat’s most common and valuable applications. It helps identify open services on a target machine. Knowing How to Use Netcat (nc) Command with Examples for scanning is fundamental. It provides quick insights into network configurations.
Scanning Specific Ports with `nc` Command
To scan a specific port, you can use Netcat in client mode. For example, to check if port 80 is open on `example.com`, you would run: `nc -zv example.com 80`. The `-z` option prevents data transfer, and `-v` provides verbose output. This quickly confirms port accessibility.
Scanning Port Ranges with Netcat for Discovery
Netcat can also scan a range of ports. This is useful for discovering all open services on a host. For instance, `nc -zv example.com 20-100` will scan ports 20 through 100. This command helps map out potential entry points or available services. It offers a comprehensive view of network exposure.
Identifying Open Ports and Services Using Netcat
When Netcat successfully connects to a port, it indicates the port is open. The verbose output often reveals additional information. This might include service banners or version numbers. Such details are crucial for understanding the target environment. Therefore, Netcat becomes a powerful reconnaissance tool.
Practical Examples: Using Netcat for Chat & File Transfer
Beyond scanning, Netcat excels at establishing direct communication channels. It facilitates simple chat applications and robust file transfers. These capabilities demonstrate its versatility. Learning How to Use Netcat (nc) Command with Examples for these tasks is highly beneficial.
Setting Up a Simple Chat Server/Client with Netcat
You can create a basic chat system using Netcat. On one machine (the server), run `nc -lvp 12345`. This listens on port 12345. On another machine (the client), connect using `nc [server_ip] 12345`. Both parties can then type messages, which appear on the other’s screen. This offers a rudimentary, direct communication method.
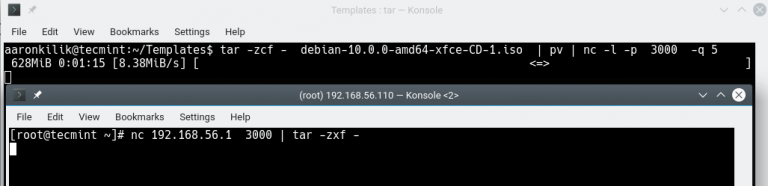
Transferring Files from Client to Server Using `nc`
File transfer is another powerful Netcat feature. To send a file from a client to a server, first set the server to listen and save incoming data: `nc -lvp 12345 > received_file.txt`. Then, from the client, send the file: `nc [server_ip] 12345 < original_file.txt`. This method is quick and efficient for direct transfers.
Transferring Files from Server to Client with Netcat
Conversely, the server can also send files to the client. On the server, prepare to send the file: `nc -lvp 12345 < file_to_send.txt`. On the client, connect and receive the file: `nc [server_ip] 12345 > received_file.txt`. This demonstrates Netcat’s flexibility in data exchange direction. It simplifies many network operations.
Practical Examples: Netcat as a Simple Web Server/Client
Netcat’s ability to handle raw TCP/IP connections makes it suitable for basic web interactions. It can simulate both server and client roles. This feature is invaluable for quick testing of HTTP requests and responses. It further solidifies How to Use Netcat (nc) Command with Examples in various scenarios.
Creating a Basic HTTP Server with `nc` Command
You can create an extremely simple HTTP server using Netcat. For example, `echo -e “HTTP/1.1 200 OKrnrnHello from Netcat!” | nc -lvp 8080`. When a browser connects to `http://[server_ip]:8080`, it will receive the “Hello from Netcat!” message. This illustrates how Netcat can serve basic content.
Making HTTP Requests with Netcat as a Client
Netcat can also act as an HTTP client. To make a GET request to a website, you can manually type the HTTP request. For instance, `echo -e “GET / HTTP/1.1rnHost: example.comrnrn” | nc example.com 80`. This sends a raw HTTP request and displays the server’s response. It’s excellent for debugging web applications.
Simulating Network Services with Netcat
Beyond HTTP, Netcat can simulate almost any network service. This is useful for testing client applications or understanding service behavior. You can set up a listener on any port and observe what data clients send. This capability makes Netcat a powerful tool for network protocol analysis. It aids in developing and troubleshooting network-dependent software.
Advanced Netcat (nc) Techniques and Security Considerations
Netcat’s power extends to more advanced techniques, often involving piping with other commands. However, this power also comes with significant security implications. Understanding these aspects is crucial. It ensures responsible and secure usage of the tool.
Using Netcat with Pipes and Other Linux Commands
Netcat truly shines when combined with other Linux commands using pipes. For instance, you can pipe the output of `ls -l` through Netcat to another machine: `ls -l | nc -lvp 12345`. On the receiving end, `nc [server_ip] 12345` will display the directory listing. This allows for powerful command execution and data transfer. You can find more examples of this on Wikipedia’s Netcat page: Netcat Wikipedia.
Netcat Backdoors and Associated Security Risks
Due to its ability to establish arbitrary connections and execute commands, Netcat can be used to create simple backdoors. For example, `nc -lvp 4444 -e /bin/bash` creates a listener that, upon connection, provides a remote shell. This is a significant security risk if exploited maliciously. Therefore, network administrators must be aware of such potential abuses.
Best Practices for Secure Netcat Usage
When using Netcat, always prioritize security. Avoid running Netcat listeners with `-e` options on production systems. Use strong authentication and encryption when transferring sensitive data, perhaps by tunneling Netcat through SSH. Always ensure you understand the implications of your commands. This proactive approach minimizes risks associated with this powerful utility.
FAQs: Common Questions About How to Use Netcat (nc) Command
What is the difference between traditional Netcat and OpenBSD Netcat?
Traditional Netcat, developed by Hobbit, is the original version. OpenBSD Netcat is a re-implementation with a focus on security and modern features. It often includes options like `-N` for graceful shutdown and improved IPv6 support. Many Linux distributions now ship with OpenBSD Netcat or a similar variant.
Can Netcat be detected by firewalls and intrusion detection systems?
Yes, Netcat can definitely be detected. Firewalls often block connections to common ports or unusual traffic patterns. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) can flag Netcat usage due to its characteristic behavior, especially when used for port scanning or shell binding. Using encrypted tunnels like SSH can help obscure Netcat traffic.
Is Netcat only for Linux, or can it be used on Windows and macOS?
Netcat is cross-platform. While it’s a staple in the Linux and Unix world, versions are readily available for Windows and macOS. The core functionality remains consistent across these operating systems. This allows users to leverage its power regardless of their preferred environment.
Conclusion: Mastering the Netcat (nc) Command for Network Tasks
Mastering How to Use Netcat (nc) Command with Examples empowers you with a versatile tool for countless network tasks. From basic port scanning and network debugging to sophisticated file transfers and simulated services, Netcat proves its worth. Its simplicity belies its profound capabilities. Therefore, it remains an essential utility in any network professional’s toolkit.
Recap of Netcat’s Versatility and Power
We’ve explored Netcat’s role as a network Swiss army knife, capable of client and server operations. Its ability to handle raw TCP/UDP connections makes it incredibly adaptable. Remember its core options and how they combine to solve complex network challenges. This powerful command-line utility is truly indispensable.
Further Learning and Practice: Your Next Steps with `nc` (CTA)
To truly master Netcat, consistent practice is key. Experiment with the examples provided and explore its man page (`man nc`) for more options. Consider setting up a small lab environment to test its capabilities safely. Share your experiences and questions in the comments below, or explore our other networking guides for more insights!
