Encountering a “docker permission denied socket” error can be a frustrating roadblock for developers and system administrators alike. This common issue prevents Docker commands from executing, effectively halting container operations. Understanding the root cause is crucial for a swift resolution. This article will thoroughly explain why this error occurs and provide actionable steps to fix it permanently, ensuring your Docker environment runs smoothly.
Understanding the Docker Permission Denied Socket Error
The “docker permission denied socket” error typically indicates that your current user lacks the necessary permissions to communicate with the Docker daemon. Docker operates as a client-server application. Your Docker client sends commands to the Docker daemon, which manages containers, images, and networks. This communication usually happens over a Unix socket.
What is the Docker Daemon Socket and Its Importance?
The Docker daemon socket, located at `/var/run/docker.sock` on Linux systems, is the primary communication channel. It acts as an endpoint for the Docker client to interact with the daemon. Therefore, proper permissions on this socket are absolutely vital. Without them, the client cannot send instructions, leading directly to a “permission denied” message.
Why This ‘Permission Denied’ Error is So Common for Docker Users
Many users encounter this specific error after a fresh Docker installation. By default, the Docker daemon runs with root privileges. Consequently, only the root user or members of the `docker` group can access its socket. If your user is not part of this special group, you will face the “docker permission denied socket” problem. Furthermore, security best practices often restrict direct root access, making this group membership essential.
Diagnosing the Root Cause of Docker Permission Denied Socket Issues
Accurately diagnosing the problem is the first step toward a lasting solution. The error message itself points to a permissions issue. However, understanding which permissions are incorrect helps in applying the right fix. This section explores the underlying mechanisms.
The Role of `/var/run/docker.sock` and Its Permissions
The `/var/run/docker.sock` file is a Unix socket, not a regular file. Its permissions dictate who can read from and write to it. Typically, it is owned by `root:docker` and has read/write permissions for the `docker` group. If these permissions are altered or your user is not in the `docker` group, access will be denied.
How User Permissions Affect Docker Daemon Interaction
When you run a Docker command, your shell executes it with your current user’s privileges. The Docker client then attempts to connect to the socket. If your user is not part of the `docker` group, the operating system denies access. This security measure prevents unauthorized users from controlling the Docker daemon. Therefore, managing user permissions is paramount.
Common Scenarios Leading to Socket Access Problems
Several situations can trigger the “docker permission denied socket” error. These often include:
- New Docker installations where the user hasn’t been added to the `docker` group.
- Running Docker commands from a new user account.
- Changes in system configuration or security policies.
- Corrupted Docker installation or daemon issues.
Understanding these scenarios helps pinpoint the exact problem quickly.
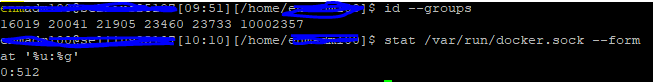
Initial Troubleshooting Steps for Docker Socket Permissions
Before implementing more permanent solutions, a few quick checks can help confirm the nature of the “docker permission denied socket” issue. These steps ensure the Docker daemon is running correctly and your system’s Basic configuration is sound.
Verifying Docker Daemon Status and Service Health
First, confirm that the Docker daemon itself is active and running. A stopped daemon will also prevent commands from working, though with a different error. You can check its status using your system’s service manager.
For most Linux distributions, use the following command:
sudo systemctl status dockerIf the service is not running, start it with `sudo systemctl start docker`. This ensures the daemon is operational before addressing permissions.
Checking Your Current User’s Group Memberships
Next, verify which groups your current user belongs to. The `docker` group is essential for non-root access. Use the `groups` command to see your affiliations.
groupsLook for `docker` in the output. If it’s missing, this is a strong indicator of the “docker permission denied socket” problem. This command provides a clear picture of your current user’s privileges.
Restarting Docker Service and Re-logging In
Sometimes, simply restarting the Docker service can resolve transient issues. Furthermore, if you’ve recently added your user to a group, you must re-authenticate your session for the changes to take effect. This often means logging out and logging back in, or even a full system reboot.
Restart the Docker service with: `sudo systemctl restart docker`.
The Recommended Fix: Adding Your User to the `docker` Group
The most common and recommended solution for the “docker permission denied socket” error involves adding your user to the `docker` group. This grants your user the necessary permissions to interact with the Docker daemon without using `sudo` for every command.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Add Your User to the `docker` Group
Follow these steps carefully to resolve the permission issue:
- Add your user: Open a terminal and execute: `sudo usermod -aG docker $USER`. This command adds your current user (`$USER`) to the `docker` group.
- Verify group addition: Confirm your user is now part of the `docker` group by running: `groups $USER`. You should see `docker` listed.
- Apply changes: Log out of your current session and log back in. Alternatively, reboot your system. This step is crucial for the new group membership to take effect.
- Test Docker: After re-logging in, try running a Docker command without `sudo`, such as: `docker run hello-world`.
If successful, you will see the “Hello from Docker!” message. This indicates the “docker permission denied socket” error is resolved.
Applying Group Changes: Re-authenticating Your Session
It’s important to understand why re-authentication is necessary. When you log in, your system caches your group memberships. Adding yourself to a new group doesn’t immediately update this Cache for your active session. Logging out and back in forces the system to re-read your group affiliations, applying the new permissions. This ensures the fix for “docker permission denied socket” takes hold.
Confirming Successful Docker Access After Group Modification
After performing the steps above, always confirm your access. Running `docker run hello-world` is the standard test. If you still encounter issues, double-check that the `docker` daemon is running and that you indeed re-logged in. Sometimes, a full system reboot is the most reliable way to ensure all changes are applied. For more information on post-installation steps, refer to the official Docker documentation (https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/).
Advanced Solutions for Persistent Docker Permission Denied Problems
While adding your user to the `docker` group resolves most “docker permission denied socket” issues, some complex environments might require further investigation. These advanced scenarios are less common but important to address.
When the `docker` Group Fix Isn’t Enough: SELinux/AppArmor Conflicts
Security enhancements like SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) or AppArmor can sometimes interfere. These systems enforce mandatory access controls, potentially overriding standard Unix permissions. If you’re still facing a “docker permission denied socket” error, check your system logs for SELinux or AppArmor denials. Adjusting their policies might be necessary, though this is an advanced task.
Understanding and Mitigating the Risks of `sudo docker`
Running `sudo docker` always works because `sudo` grants root privileges. However, this is generally discouraged for regular operations. Using `sudo` with Docker effectively gives the container root access to your host system. This poses a significant security risk. Therefore, fixing the “docker permission denied socket” error by adding your user to the `docker` group is the preferred and safer approach.
Considerations for Rootless Docker and Alternative Setups
For enhanced security, some users opt for Rootless Docker. This setup runs the Docker daemon and containers as a non-root user. While it avoids the `docker permission denied socket` issue by design for the root user, it introduces its own set of configuration challenges. Understanding your Docker setup is key to troubleshooting effectively.
Preventing Future Docker Permission Denied Socket Errors
Proactive measures can help avoid the “docker permission denied socket” error from recurring. Establishing good practices for user management and system maintenance is crucial for a stable Docker environment.
Best Practices for Docker User Management and Security
Always ensure that new users who need Docker access are properly added to the `docker` group. Furthermore, regularly review your system’s user and group configurations. Limiting the number of users in the `docker` group enhances security. This prevents unauthorized access to the Docker daemon.
Maintaining Correct Permissions on `/var/run/docker.sock`
Avoid manually changing the permissions of `/var/run/docker.sock`. Docker itself manages these permissions correctly upon installation and daemon startup. If you suspect corruption, reinstalling Docker or restarting the daemon is usually safer than direct `chmod` commands. Incorrect manual changes can exacerbate the “docker permission denied socket” problem.
Regular System Updates and Docker Daemon Configuration Checks
Keeping your operating system and Docker installation updated is vital. Updates often include security patches and bug fixes that can prevent permission-related issues. Periodically review your Docker daemon configuration files for any unintended changes. Consistent maintenance helps prevent unexpected “docker permission denied socket” occurrences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do I still get ‘permission denied’ after adding to the `docker` group?
This usually means you haven’t fully re-authenticated your session. You must log out and log back in (or reboot) for the new group membership to take effect. The system needs to refresh your user’s group affiliations. Always verify your group membership with the `groups` command after re-logging in.
Is it ever safe to change the permissions of `/var/run/docker.sock` directly?
Generally, no. Manually changing the permissions of `/var/run/docker.sock` with `chmod` is a temporary workaround and can introduce security vulnerabilities. It’s much safer and more robust to add your user to the `docker` group. The daemon itself manages the socket’s permissions, and direct changes can be overwritten or lead to instability.
How can I verify my user’s group memberships on Linux?
You can easily check your current user’s group memberships by opening a terminal and typing `groups`. To check another user’s groups, use `groups `. This command lists all groups that the specified user belongs to. This is a quick way to confirm if your user is in the `docker` group.
Conclusion: Resolve Your Docker Permission Denied Socket Problems Permanently
The “docker permission denied socket” error is a common but easily resolvable issue. It stems from insufficient user permissions to access the Docker daemon’s Unix socket. By understanding the role of `/var/run/docker.sock` and properly managing user group memberships, you can quickly overcome this obstacle. The most effective solution involves adding your user to the `docker` group and re-authenticating your session.
Key Takeaways for Managing Docker Socket Access
Always prioritize adding users to the `docker` group for non-root access. Avoid using `sudo docker` for routine tasks due to security implications. Furthermore, maintain good system hygiene with regular updates and configuration checks. These practices ensure a secure and functional Docker environment, free from persistent “docker permission denied socket” errors.
Empowering Your Docker Workflow with Correct Permissions
Resolving the “docker permission denied socket” error empowers you to seamlessly integrate Docker into your development and deployment workflows. With proper permissions, you can manage containers efficiently and securely. Take action today to implement these fixes and enhance your Docker experience. Share this guide with others who might be struggling with similar Docker permission issues!
